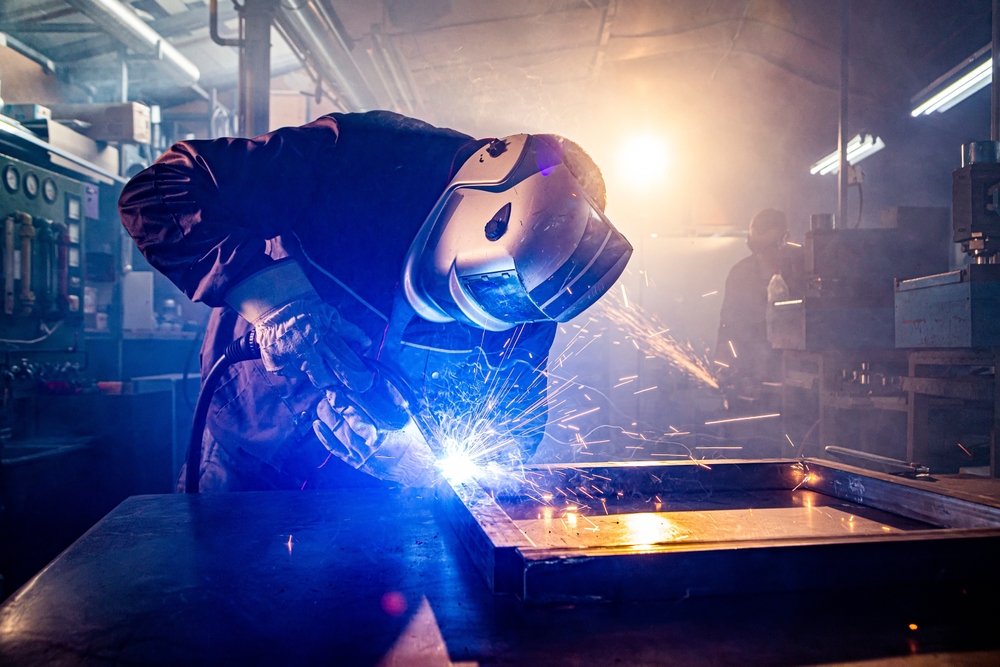
Metal fabrication plays an integral role in the world of industrial applications. From construction to aerospace, the metal fabrication process has been a cornerstone of technological advancement. This blog delves into the significance of metal fabrication, its methodologies, and its implications for modern industries.
What is Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication is the process of building machines, structures, and components from raw metal materials. It involves a range of processes including cutting, bending, welding, and assembling to transform metals into useful products. Whether creating intricate parts for machinery or large-scale industrial components, the metal fabrication process ensures precision and durability.
Key Steps in the Metal Fabrication Process
The metal fabrication process comprises several critical steps, each ensuring the final product meets the desired specifications:
- Design and Engineering: Utilizing CAD software, engineers create detailed blueprints to guide the fabrication process.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate metal, such as steel, aluminum, or copper, depending on the application requirements.
- Cutting: Employing tools like lasers, plasma cutters, or saws to shape the raw material.
- Forming and Bending: Using press brakes and other machinery to bend metal into desired shapes.
- Welding and Joining: Connecting different metal parts through advanced welding techniques.
- Finishing: Applying treatments such as painting, coating, or polishing for enhanced aesthetics and durability.
The Role of Metal Fabrication in Industrial Applications
Industrial sectors rely heavily on metal fabrication for creating components that withstand high-stress environments. Here are some key industries and how they benefit:
Construction
In the construction industry, metal fabrication is essential for producing steel beams, columns, and other structural components. These elements form the backbone of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure. Fabricated metal ensures:
- High load-bearing capacity.
- Resistance to environmental factors like corrosion.
- Longevity, even in extreme conditions.
Automotive
The automotive industry leverages metal fabrication to manufacture parts such as frames, exhaust systems, and engine components. Precision machining ensures:
- Reduced weight for improved fuel efficiency.
- Enhanced safety and durability.
- Cost-effective production with minimal waste.
Aerospace
In aerospace, the demand for lightweight yet strong materials is critical. The metal fabrication process in this sector involves advanced techniques like CNC machining and laser cutting. Benefits include:
- High-performance parts capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and pressures.
- Customization to meet stringent safety and design standards.
- Improved aerodynamics through precise component shaping.
Energy and Utilities
Metal fabrication supports the energy sector by creating components for wind turbines, pipelines, and power plants. Industrial machining ensures reliability and efficiency, contributing to sustainable energy solutions.
Manufacturing and Machinery
For manufacturing industries, metal fabrication produces tools, equipment, and machine parts essential for operational efficiency. Industrial machining aids in:
- Custom production tailored to specific operational needs.
- Durability and precision in heavy-duty applications.
- Scalability to meet growing industry demands.
Advancements in Metal Fabrication Technology
Modern advancements have revolutionized the metal fabrication process, making it more efficient and versatile. Key technologies include:
CNC Machining
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining automates the fabrication process, delivering unparalleled precision. It enables:
- Intricate designs with minimal human intervention.
- Faster production cycles.
- Consistency across large-scale manufacturing.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting offers exceptional accuracy and speed, reducing material waste. It is ideal for:
- Complex geometries.
- High-volume production.
- Achieving smooth edges without additional finishing.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing complements traditional metal fabrication by allowing for:
- Rapid prototyping.
- Customization of parts.
- Reduced lead times and production costs.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics in fabrication ensures efficiency and safety. Automated welding and material handling improve:
- Production speed.
- Consistency and accuracy.
- Worker safety by reducing manual labor in hazardous environments.
Challenges in Metal Fabrication
Despite its benefits, the metal fabrication process faces challenges that industries must address:
Material Costs
The fluctuating costs of raw materials like steel and aluminum can impact project budgets. Strategic sourcing and recycling initiatives can help mitigate these challenges.
Skilled Workforce Shortages
As the industry evolves with new technologies, finding skilled labor proficient in both traditional and modern techniques can be a hurdle. Investment in training and education is critical.
Environmental Impact
Metal fabrication involves processes that may produce waste and emissions. Adopting sustainable practices like recycling scrap metal and using eco-friendly coatings can reduce the environmental footprint.
The Future of Metal Fabrication
The future of metal fabrication lies in continued innovation and sustainability. Trends shaping the industry include:
Smart Factories
Integration of IoT and AI technologies in fabrication facilities allows real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, optimizing efficiency and reducing downtime.
Sustainable Practices
Green fabrication techniques, such as utilizing renewable energy in production and minimizing waste, are becoming standard in response to environmental concerns.
Advanced Materials
The development of high-strength, lightweight alloys opens new possibilities for industries like aerospace and automotive.
Global Collaboration
With globalization, companies are leveraging expertise and resources across borders, fostering innovation and cost-effectiveness in the metal fabrication process.
Conclusion
The metal fabrication process is a cornerstone of industrial applications, driving progress in sectors ranging from construction to aerospace. As technology advances and industries prioritize sustainability, metal fabrication will continue to adapt, delivering innovative solutions to meet global demands. By embracing modern techniques and overcoming challenges, this field will remain a vital part of industrial and economic growth.
Need an Industrial Machine Shop in Baton Rouge, LA?
Established in 1956, our team here at Metal Works Corporation is an A.S.M.E. certified industrial fabrication company specializing in pipe and tube bending, pipe fabrication, coiling, vessel fabrication, and welding for major industries. Our in house’ machine shop has unique capabilities and produces specialty springs of all alloys, custom rotating mechanical seals, and various other industrial components. We appreciate our customers and work to forge lasting relationships built on trust and reliability. Contact us today and allow our team to be the shortest distance between problem and solution for your unique industrial requirements.